1. Introduction & Overview
What is a Nonce?
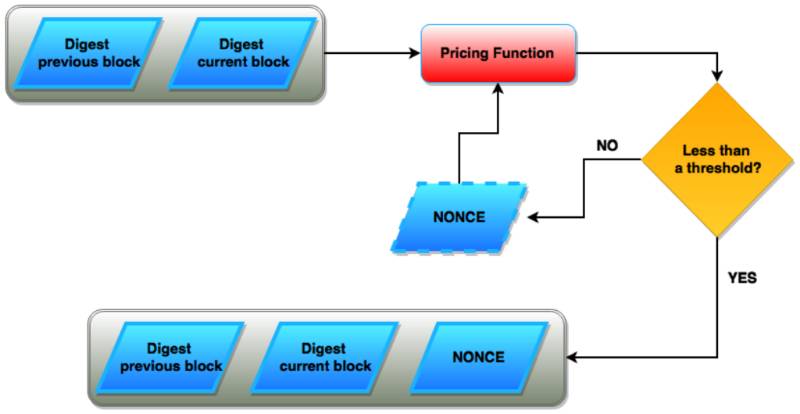
- Definition:
A Nonce (short for Number Used Once) is a cryptographic value used once to ensure uniqueness in a transaction or data block. In the context of cryptoblockcoins, it is primarily used in proof-of-work (PoW) systems to achieve consensus and secure the blockchain. - Key Characteristics:
- Unique for each block
- Helps achieve the required hash difficulty
- Integral to mining and transaction security
History / Background
- Early cryptography systems introduced the concept of nonces to prevent replay attacks.
- In Bitcoin (2009) and other PoW blockchains, the nonce became central for miners trying to solve hash puzzles and validate blocks.
Relevance in Cryptoblockcoins
- Ensures block uniqueness
- Maintains integrity of blockchain
- Prevents double-spending attacks
- Enables difficulty adjustment by miners
- Plays a role in consensus mechanisms
2. Core Concepts & Terminology
| Term | Definition | Relevance in Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Nonce | Number used once for cryptographic purposes | Ensures each block’s hash is unique |
| Hash | Fixed-length cryptographic digest of input | Nonce is modified to change the hash output |
| Proof-of-Work (PoW) | Mining algorithm for block validation | Miners vary nonce to meet target difficulty |
| Target Difficulty | Threshold value that a block hash must meet | Nonce search continues until hash < target |
| Miner | Node attempting to add new block | Uses nonce to find valid block hash |
Lifecycle Fit:
- Transaction Creation → Transactions are bundled into a block
- Nonce Assignment → Miner sets nonce starting at 0
- Hash Calculation → Block data + nonce hashed
- Validation → Hash compared against target
- Adjustment → If hash invalid, increment nonce and retry
3. Architecture & How It Works
Components & Internal Workflow
Block Mining Process:
- Block Header Formation:
- Includes previous block hash, Merkle root, timestamp, and nonce.
- Nonce Iteration:
- Miner starts with nonce = 0, hashes block header
- If hash < difficulty target → block valid
- Else → increment nonce and retry
- Block Broadcast:
- Valid block is broadcast to network
- Consensus:
- Other nodes verify nonce and block validity
Internal Workflow Diagram:
+-------------------+
| Pending Block |
| Transactions |
+--------+----------+
|
v
+-------------------+
| Block Header |
| (includes Nonce) |
+--------+----------+
|
v
+-------------------+
| Hash Function |
| SHA-256 / Keccak |
+--------+----------+
|
v
+-------------------+
| Check Target |
| (Difficulty) |
+--------+----------+
| Yes / No
v
+-------------------+
| Block Accepted |
+-------------------+
If diagram images are preferred for documentation, a flowchart using rectangles and decision diamonds can represent the same process.
Integration Points with CI/CD or Cloud Tools
- Blockchain Testing:
Nonces are simulated in test networks (Testnet) using scripts in CI/CD pipelines. - Monitoring & Analytics:
Cloud tools can track nonce retries and mining efficiency. - Smart Contract Interaction:
In Ethereum, nonce ensures transaction order is maintained per account.
4. Installation & Getting Started
Basic Setup / Prerequisites
- Node.js / Python / Go installed (for blockchain client)
- Access to a blockchain client (Bitcoin Core, Geth for Ethereum)
- Basic understanding of cryptography and hashes
Hands-On: Step-by-Step Beginner Guide
Example: Mining a Block with Nonce in Python (simplified PoW)
import hashlib
# Sample Block Data
block_data = "Block #1 | Transactions: Alice->Bob 10 BTC"
nonce = 0
difficulty = 4 # Number of leading zeros
while True:
text = block_data + str(nonce)
block_hash = hashlib.sha256(text.encode()).hexdigest()
if block_hash.startswith('0' * difficulty):
print(f"Valid nonce found: {nonce}")
print(f"Hash: {block_hash}")
break
else:
nonce += 1
Explanation:
- Miner tries different nonce values until hash meets difficulty
- Shows how the nonce ensures uniqueness and PoW validation
5. Real-World Use Cases
Cryptocurrencies
| Coin | Nonce Role | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Bitcoin | PoW mining | Miners increment nonce to solve hash puzzle |
| Ethereum (pre-merge) | PoW mining | Nonce in block header for mining validation |
| Litecoin | PoW mining | Faster block generation using nonce |
| Dogecoin | Merged mining | Shares nonce space with Litecoin |
Industry-Specific Examples
- Supply Chain: Nonce ensures unique block for each shipment
- Voting Systems: Nonce prevents duplicate voting records
- Finance / Banking: Nonce prevents replay attacks in smart contracts
6. Benefits & Limitations
Key Advantages
- Guarantees block uniqueness
- Prevents replay attacks
- Integral to PoW security
- Supports difficulty adjustment and network stability
Common Challenges
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| High computational cost | Miners must try many nonces |
| Energy consumption | PoW mining uses significant power |
| Nonce exhaustion | Extremely rare in high-difficulty scenarios, but possible |
7. Best Practices & Recommendations
- Use cryptographically secure random nonces for custom applications
- Monitor nonce iteration rates for mining performance
- Use incremental nonce tracking in smart contracts to prevent double-spending
- Align compliance with blockchain standards (Bitcoin, Ethereum)
8. Comparison with Alternatives
| Feature | Nonce | Timestamp / Sequence Number | Random Salt |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Unique value for block or transaction | Order or time-based uniqueness | Adds entropy to hashes |
| Use Case | PoW mining, transaction validation | Transaction ordering | Password hashing, cryptography |
| Security | High | Medium | High |
| Deterministic | Incremented or calculated | True | Random |
When to Choose Nonce:
- Proof-of-Work systems
- Preventing replay attacks
- Ensuring unique transaction or block hash
9. Conclusion
- Nonce is a cornerstone of blockchain security and consensus.
- Enables uniqueness, proof-of-work, and transaction integrity.
- Future trends include:
- Nonce management in Proof-of-Stake (PoS) systems
- Optimized nonce calculation for energy-efficient mining
- Use in cross-chain and layer-2 solutions
Next Steps for Learners:
- Implement nonce in a personal blockchain project
- Monitor nonce-related performance metrics in mining nodes
- Explore advanced PoW alternatives (e.g., ASIC-resistant mining)
Official Documentation & Communities:
- Bitcoin Developer Docs: Block Header
- Ethereum Documentation: Nonce
- StackExchange Bitcoin
- Reddit r/cryptodevs
Category: