1. Introduction & Overview
What is Ethereum?
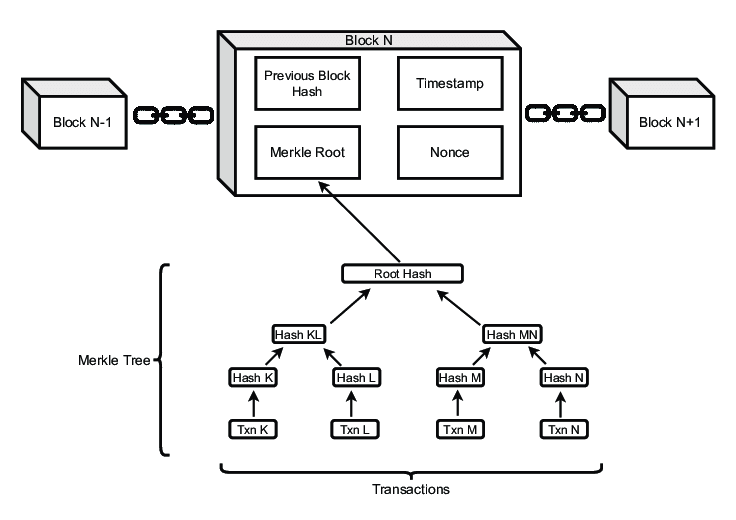
- Ethereum is a decentralized, open-source blockchain platform.
- It supports smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps).
- Native cryptocurrency: Ether (ETH).
- Unlike Bitcoin (focused on peer-to-peer payments), Ethereum acts as a programmable blockchain.
History / Background
- Proposed in 2013 by Vitalik Buterin.
- Launched in 2015 with the help of co-founders like Gavin Wood and Joseph Lubin.
- Ethereum introduced the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), enabling developers to build dApps.
- Major upgrades:
- Ethereum 1.0 – Proof of Work consensus.
- Ethereum 2.0 (The Merge, 2022) – Shift to Proof of Stake (energy-efficient).
Why is it Relevant in Cryptoblockcoins?
- Powers 70%+ of DeFi (Decentralized Finance) ecosystem.
- Backbone for NFTs, DAOs, metaverse projects.
- Enables tokenization (ERC-20, ERC-721, ERC-1155).
- High developer adoption → fastest-growing blockchain ecosystem.
2. Core Concepts & Terminology
| Term | Definition | Importance in Lifecycle |
|---|---|---|
| Ether (ETH) | Native cryptocurrency | Used for gas fees, staking, transactions |
| Gas | Fee required to perform a transaction or execute a contract | Regulates blockchain workload |
| Smart Contract | Self-executing contract coded on blockchain | Automates agreements |
| dApp | Decentralized application | Runs without central authority |
| EVM | Ethereum Virtual Machine | Executes smart contracts |
| ERC Standards | Token standards (ERC-20, ERC-721, etc.) | Ensure interoperability |
Lifecycle Fit in Cryptoblockcoins:
- Creation – Deploy smart contracts.
- Transaction – Users pay gas in ETH.
- Validation – Validators confirm transactions under Proof of Stake.
- Execution – dApps interact via EVM.
- Settlement – Immutable record on Ethereum blockchain.
3. Architecture & How It Works
Components of Ethereum
- Application Layer: dApps, wallets (MetaMask, TrustWallet).
- Smart Contract Layer: Solidity contracts, deployed via EVM.
- Consensus Layer: Proof of Stake validators.
- Data Layer: Distributed ledger (blockchain).
- Networking Layer: Peer-to-peer communication.
Workflow (Transaction Lifecycle)
- User initiates transaction (e.g., send ETH, mint NFT).
- Wallet signs transaction with private key.
- Transaction broadcast to network.
- Validators (PoS) verify & propose block.
- EVM executes smart contract logic.
- Transaction finalized & stored permanently.
Architecture Diagram (Textual Representation)
+-------------------------------------------------------------+
| Application Layer (dApps) |
| - Wallets, DeFi apps, NFT marketplaces |
+--------------------------+----------------------------------+
| Smart Contract Layer| (Solidity, Vyper) |
| - EVM executes contracts securely |
+--------------------------+----------------------------------+
| Consensus Layer (Proof of Stake Validators) |
| - Block proposal, attestation, finalization |
+-------------------------------------------------------------+
| Data Layer (Blockchain Ledger) |
| - Immutable records, transaction history |
+-------------------------------------------------------------+
| Networking Layer (P2P Nodes) |
| - Node communication, gossip protocol |
+-------------------------------------------------------------+
Integration with CI/CD or Cloud
- CI/CD: Smart contract deployment pipelines using GitHub Actions, Hardhat, or Truffle.
- Cloud Tools: AWS Blockchain Templates, Azure Blockchain Service, Infura (Ethereum nodes as service).
4. Installation & Getting Started
Prerequisites
- Node.js (for Hardhat/Truffle).
- Ethereum wallet (MetaMask).
- Infura/Alchemy account for node access.
- Basic Solidity knowledge.
Step-by-Step Setup Guide
- Install Node.js
sudo apt update
sudo apt install nodejs npm
2. Install Hardhat (Ethereum dev environment)
mkdir ethereum-demo
cd ethereum-demo
npm init -y
npm install --save-dev hardhat
npx hardhat
3. Create a Sample Project → Choose “Create a basic sample project”.
4. Compile Smart Contract
npx hardhat compile
5. Deploy to Testnet (Goerli/ Sepolia)
- Get free test ETH from faucet.
- Configure in
hardhat.config.js. - Run:
npx hardhat run scripts/deploy.js --network sepolia
6. Interact with Contract using MetaMask or scripts.
5. Real-World Use Cases
- DeFi (Decentralized Finance)
- Lending & borrowing (Aave, Compound).
- Decentralized exchanges (Uniswap).
- NFT Marketplaces
- Minting & trading digital art (OpenSea, Rarible).
- DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations)
- Governance platforms (MakerDAO, Aragon).
- Enterprise Blockchain
- Supply chain (IBM Food Trust), real estate tokenization.
6. Benefits & Limitations
Benefits
- Decentralized, censorship-resistant.
- Huge developer ecosystem.
- Smart contracts enable automation.
- Large liquidity (ETH widely accepted).
Limitations
- Scalability: Limited transactions per second.
- Gas Fees: Can be expensive.
- Complexity: Steeper learning curve than Bitcoin.
- Energy Use (before Merge): Now improved with PoS.
7. Best Practices & Recommendations
- Security: Audit smart contracts (use OpenZeppelin).
- Performance: Use Layer-2 (Arbitrum, Optimism) for scaling.
- Compliance: Ensure alignment with KYC/AML when building fintech dApps.
- Automation: Use CI/CD pipelines for contract deployment.
8. Comparison with Alternatives
| Feature | Ethereum | Solana | Binance Smart Chain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consensus | Proof of Stake | Proof of History + PoS | PoS Authority |
| TPS | ~15–30 | ~65,000 | ~160 |
| Fees | High (varies) | Low | Low |
| Ecosystem | Largest (DeFi, NFT, DAO) | Fast but younger | Strong Binance-backed |
| Dev Tools | Mature (Hardhat, Truffle) | Growing | Limited vs Ethereum |
When to Choose Ethereum?
- When decentralization and security > speed.
- When you want ecosystem richness.
- For NFT/DeFi where liquidity is key.
9. Conclusion
- Ethereum is the cornerstone of cryptoblockcoins.
- Future trends: Ethereum 2.0 scaling, sharding, rollups, zk-EVMs.
- Ideal for developers building decentralized ecosystems.
📌 Next Steps:
- Visit official docs: https://ethereum.org/en/developers/
- Join communities: Reddit (/r/ethereum), Ethereum Discord, StackExchange.
- Practice by deploying your first smart contract on a testnet.
Category: